Difference between revisions of "Anime"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Copal is a name given to tree [[resin]] that is particularly identified with the aromatic resins used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and other purposes. More generally, the term copal describes resinous substances in an intermediate stage of polymerization and hardening between "gummier" resins and amber. The word copal is derived from the Nahuatl language word copalli, meaning "incense".<br><br> | Copal is a name given to tree [[resin]] that is particularly identified with the aromatic resins used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and other purposes. More generally, the term copal describes resinous substances in an intermediate stage of polymerization and hardening between "gummier" resins and amber. The word copal is derived from the Nahuatl language word copalli, meaning "incense".<br><br> | ||
Copal is still used by a number of indigenous peoples of Mexico and Central America as an incense and during sweat lodge ceremonies. It is available in different forms. The hard, amber-like yellow copal is a less expensive version. The white copal, a hard, milky, sticky substance, is a more expensive version of the same resin.<br><br> | Copal is still used by a number of indigenous peoples of Mexico and Central America as an incense and during sweat lodge ceremonies. It is available in different forms. The hard, amber-like yellow copal is a less expensive version. The white copal, a hard, milky, sticky substance, is a more expensive version of the same resin.<br><br> | ||
| − | Copal was also grown in East Africa (the common species there being Hymenaea verrucosa), initially feeding an Indian Ocean demand for incense. By the | + | Copal was also grown in East Africa (the common species there being Hymenaea verrucosa), initially feeding an Indian Ocean demand for incense. By the 18<sup>th</sup> Century, Europeans found it to be a valuable ingredient in making a good wood varnish. It became widely used in the manufacture of [[furniture]] and carriages. It was also sometimes used as a picture varnish. By the late 19th and early 20<sup>th</sup> century varnish manufacturers in England and America were using it on train carriages, greatly swelling its demand. |
In 1859 Americans consumed 68 percent of the East African trade, which was controlled through the Sultan of Zanzibar, with Germany receiving 24 percent. The American Civil War and the creation of the Suez Canal led to Germany, India and Hong Kong taking the majority by the end of that century.<br><br> | In 1859 Americans consumed 68 percent of the East African trade, which was controlled through the Sultan of Zanzibar, with Germany receiving 24 percent. The American Civil War and the creation of the Suez Canal led to Germany, India and Hong Kong taking the majority by the end of that century.<br><br> | ||
East Africa apparently had a higher amount of subfossil copal, which is found one or two meters below living copal trees from [[roots]] of trees that may have lived thousands of years earlier. This subfossil copal produces a harder varnish. Subfossil copal is also well-known from New Zealand (Kauri gum), Japan, the Dominican Republic, Colombia and Madagascar. It often has inclusions and is sometimes sold as "young amber". Copal can be easily distinguished from genuine amber by its lighter citrine colour and its surface getting tacky with a drop of [[acetone]] or chloroform.<br><br> | East Africa apparently had a higher amount of subfossil copal, which is found one or two meters below living copal trees from [[roots]] of trees that may have lived thousands of years earlier. This subfossil copal produces a harder varnish. Subfossil copal is also well-known from New Zealand (Kauri gum), Japan, the Dominican Republic, Colombia and Madagascar. It often has inclusions and is sometimes sold as "young amber". Copal can be easily distinguished from genuine amber by its lighter citrine colour and its surface getting tacky with a drop of [[acetone]] or chloroform.<br><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:11, 3 October 2012
| Infobox on Anime | |
|---|---|
| Example of Anime | 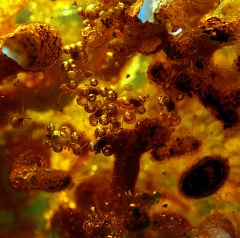 |
| Facts | |
| Origin |
|
| Stowage factor (in m3/t) | - |
| Humidity / moisture | - |
| Ventilation | - |
| Risk factors |
|
Anime
Description
Copal is a name given to tree resin that is particularly identified with the aromatic resins used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and other purposes. More generally, the term copal describes resinous substances in an intermediate stage of polymerization and hardening between "gummier" resins and amber. The word copal is derived from the Nahuatl language word copalli, meaning "incense".
Copal is still used by a number of indigenous peoples of Mexico and Central America as an incense and during sweat lodge ceremonies. It is available in different forms. The hard, amber-like yellow copal is a less expensive version. The white copal, a hard, milky, sticky substance, is a more expensive version of the same resin.
Copal was also grown in East Africa (the common species there being Hymenaea verrucosa), initially feeding an Indian Ocean demand for incense. By the 18th Century, Europeans found it to be a valuable ingredient in making a good wood varnish. It became widely used in the manufacture of furniture and carriages. It was also sometimes used as a picture varnish. By the late 19th and early 20th century varnish manufacturers in England and America were using it on train carriages, greatly swelling its demand.
In 1859 Americans consumed 68 percent of the East African trade, which was controlled through the Sultan of Zanzibar, with Germany receiving 24 percent. The American Civil War and the creation of the Suez Canal led to Germany, India and Hong Kong taking the majority by the end of that century.
East Africa apparently had a higher amount of subfossil copal, which is found one or two meters below living copal trees from roots of trees that may have lived thousands of years earlier. This subfossil copal produces a harder varnish. Subfossil copal is also well-known from New Zealand (Kauri gum), Japan, the Dominican Republic, Colombia and Madagascar. It often has inclusions and is sometimes sold as "young amber". Copal can be easily distinguished from genuine amber by its lighter citrine colour and its surface getting tacky with a drop of acetone or chloroform.
Application
A yellow transparent resin used in the manufacture of resins and lacquers.
Shipment/storage
Usually packed in cases.
Risk factors
- Liable to heat and give off moisture
- Subject to loss in weight due to chafing











